Part I
Nobody wants to hear that a collision just happened, but instead that a collision can be avoided. Real-time collision detection running on the CNC controller finds and prevents collisions before they happen.
This two part article explains why collision avoidance on the CNC machine is indispensable and how you can ensure real-time performance, even on CNC controllers with less powerful processors.
The need for real-time collision checking on the machine
As machining processes become more and more sophisticated, the risk of collisions between the tool, workpiece and machine components increases. Collisions mean costly downtime and cause expensive damage to the workpiece, spindles and sometimes even the whole machine.
Most CAD/CAM vendors provide simulation software to check the toolpath for collisions before it is sent as NC code to the machine. But there is no guarantee that the real machine behaves exactly like the simulation. The simulation and the machine might interpret an NC command differently and produce different tool movements, or perhaps the operator has used a different size tool to the one in the simulation. Jog-mode is another risk because no CAM or NC based simulation can predict collisions that might result from the manual adjustment of the machine axes. These types of collisions are particularly common on complex mill-turn machines where the axes and machine components are close together. Then there is all the NC code that is programmed on the shop floor: even if these programs are simple, they have not been verified and can contain a potential collision.
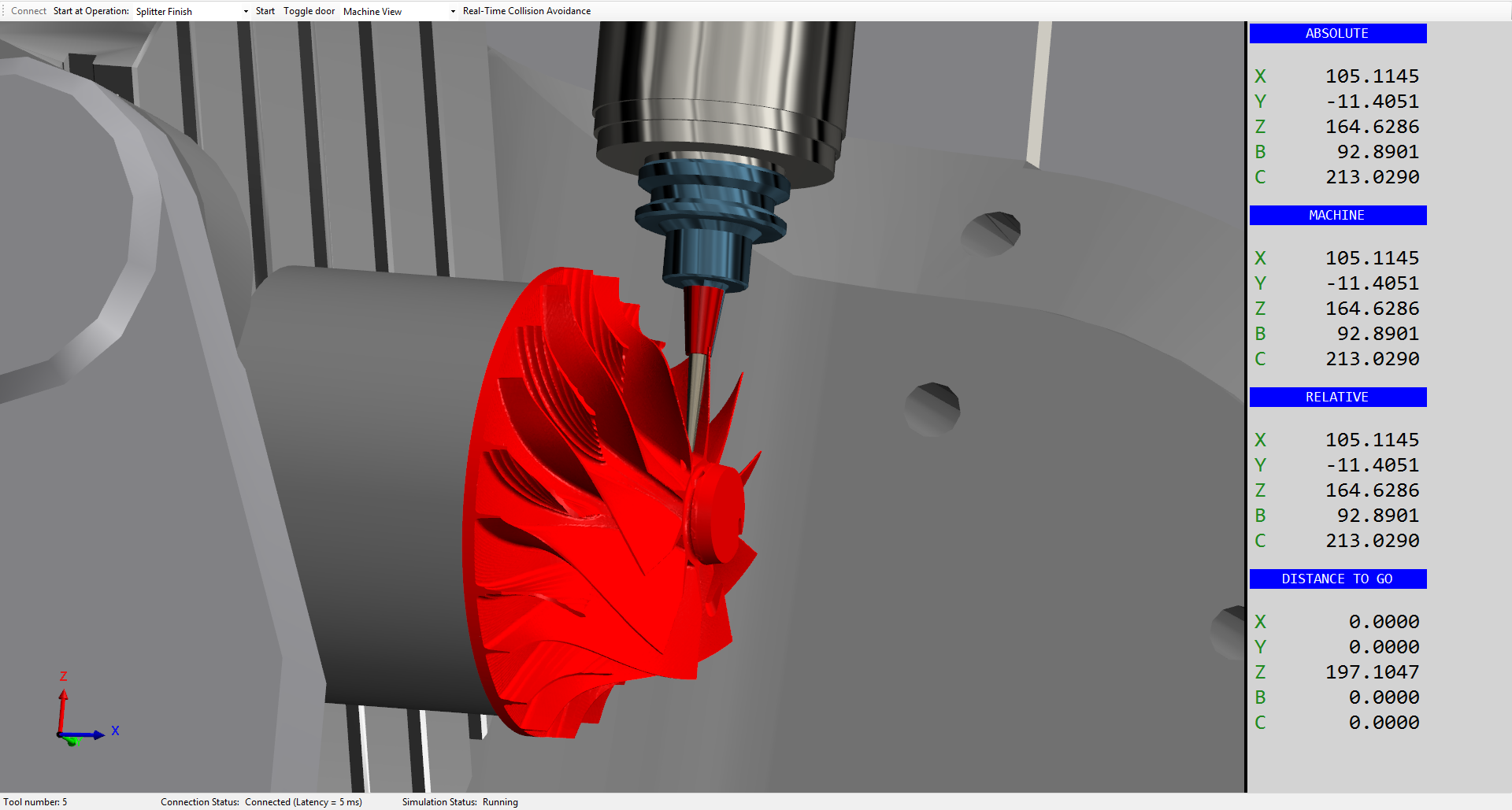
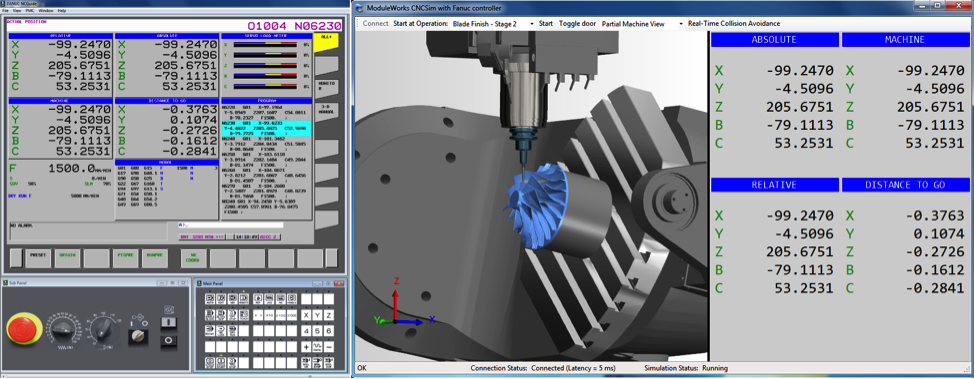
ModuleWorks CNC simulation technology
The best way to ensure collision-free machining is to implement additional, real-time collision detection on the CNC controller. ModuleWorks CNC simulation is real-time collision avoidance software that runs directly on the CNC controller to provide verification and clash detection during the milling and turning process. Because it runs on the controller, it takes the real axis positions, machine geometries and workpiece position into account. It runs the same NC code as the machine but at a faster speed to detect collisions before they happen and inform the CNC controller to stop the machine before a collision occurs.
Real-time behavior is possible even on non-real-time operating systems thanks to the look-ahead buffer provided by the CNC core. This enables asynchronous collision checking which allows for the jitter that is experienced on standard operating systems.
Nonetheless, the performance of the CNC processor remains a limiting factor for real-time behavior. But there are measures you can take to accelerate the performance of the simulation software to achieve real-time response, even on less powerful processors.
These will be covered in the next article.
About ModuleWorks
ModuleWorks is a software component provider for the CAD/CAM industry. ModuleWorks’ expertise in toolpath creation and simulation is recognized throughout the CAM industry and its software components and development services are used by the majority of the leading CAM vendors. ModuleWorks has also been leading the trend towards the adoption of this technology on CNC Controls and has many established partners in the CNC and Machine Tool Manufacturing industries.