Software Release 2025.12 Highlights
ModuleWorks 2025.12 contains a range of new features for smarter, safer and more efficient manufacturing. Highlights include new advances in 5-axis roughing and adaptive toolpath strategies as well as accelerated simulation performance. With enhanced collision detection and real-time feedback, users can fine-tune processes, increase efficiency and minimize costly mistakes. This update also offers improved support for complex geometries and a more intuitive interface, making it easier to handle complex projects. Discover all the highlights below.
Toolpath
Multi-Axis Surface Finishing | Wall, Floor and Rest Finishing
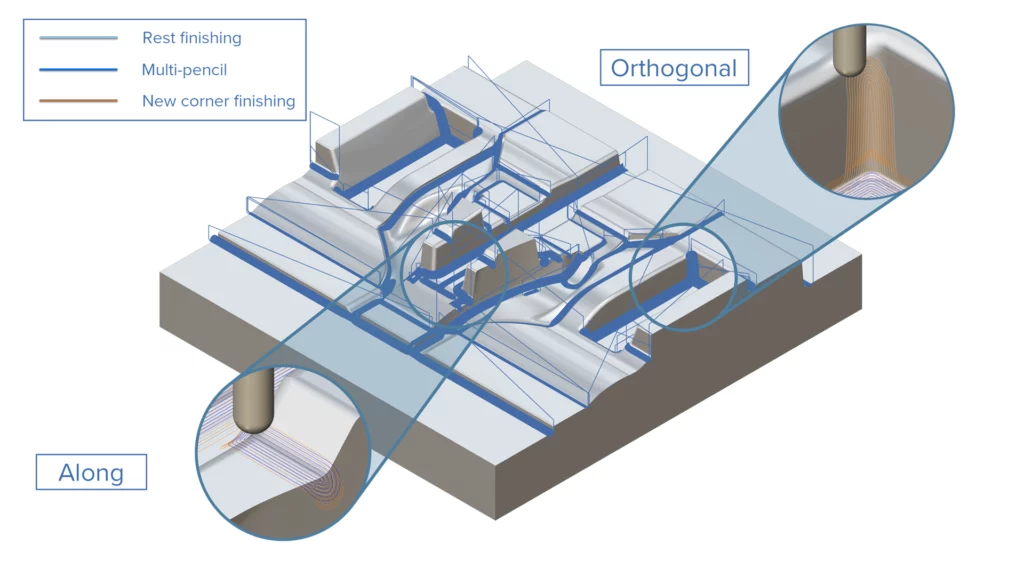
Improved Rest Finishing for Wall, Floor and Rest Finishing
Challenge: Despite advances in finishing toolpaths, significant time is still needed for manually post-processing the left over areas.
Solution: ModuleWorks 2025.12 improves the efficiency of rest finishing complex contours and areas by automating the cumbersome post-processing steps.
Benefits: The enhanced rest finishing feature delivers superior surface quality combined with ease of use and a noticeable reduction in post-processing time.
Multi-Axis Surface Finishing | Swarf Machining
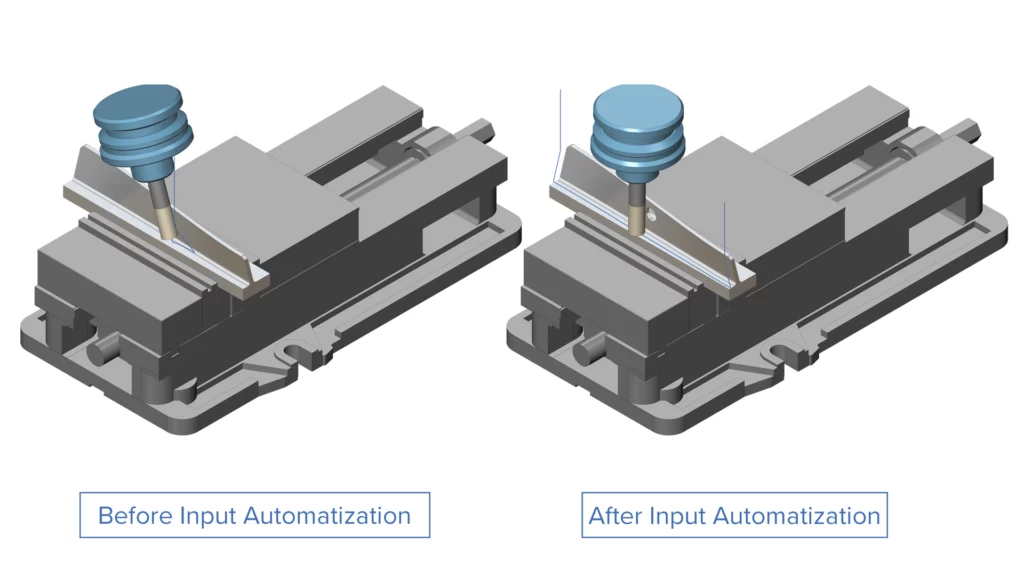
Swarf Machining - Input Automatization
Challenge: Previously, Swarf heuristics could struggle to find a guide curve on surfaces with boundaries that have round corners.
Solution: Now, Swarf Machining comes with improved logic to detect proper guide curves on the surfaces, even with surfaces that have rounded corners.
Benefits: This new feature makes programming faster and more adaptable to a wide range of part topologies.
Multi-Axis Surface Finishing | Mold and Die Finishing
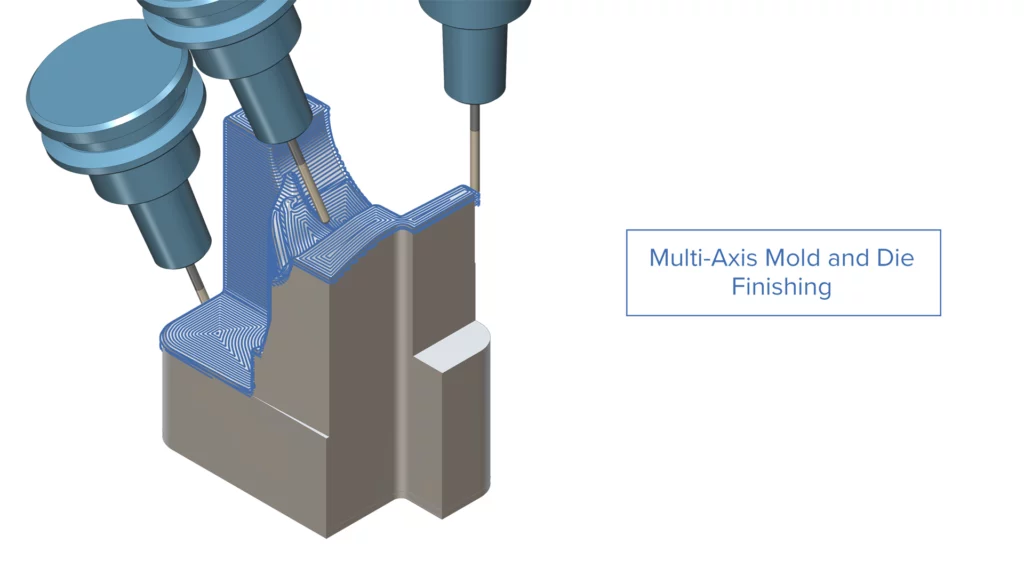
Multi-Axis Mold and Die
Challenge: Finding effective machining directions, setting up independent 3-axis operations along these machining directions and linking between them is tedious and requires high manual effort.
Solution: With automated direction detection, it’s now possible to finish a part from all desired orientations. The intelligent fallback sequence from 3-axis to 5-axis machining makes the process robust and flexible, delivering a seamless, single workflow that ensures proper linking between tool positions.
Benefits: This new feature enables faster programming of mold and die parts, reduces machining time, and offers a user-friendly interface for greater efficiency and an improved overall experience.
Multi-Axis Edge Finishing | Deburring
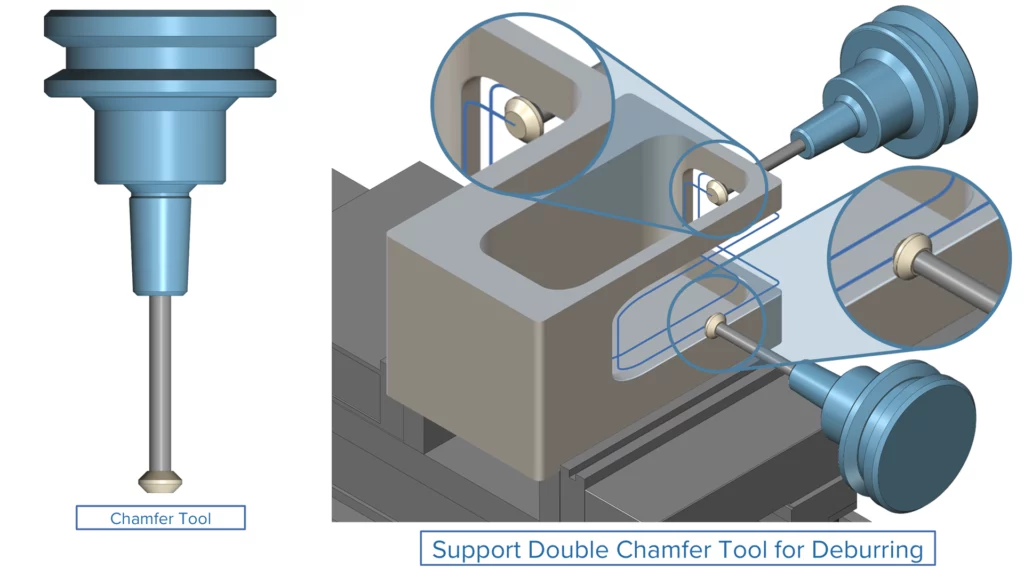
Double Chamfer Tool for Deburring
Challenge: Previously, users needed to create separate operations with two different tools to deburr edges on the top and underside of a part. This resulted in additional effort and increased programming time.
Solution: Now, it is possible to deburr both the upper and lower edges of a part using a double chamfer tool. The system automatically chooses whether to apply the tool’s upper or lower chamfer to each contour.
Benefits: This feature speeds up the programming process and makes it more efficient.
Core Component Technologies | FeedControl
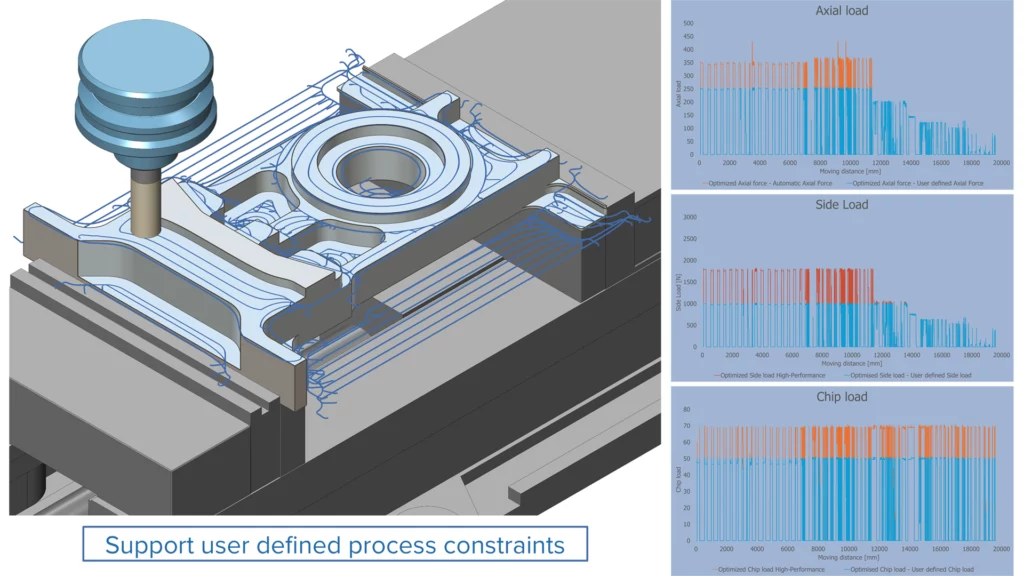
User Defined Process Constraints
Challenge: Currently, users are not able to adjust the automatic settings. However, in some machining scenarios it is important to be able to manually control the values.
Solution: This feature enables users to define their own process constraints within the FeedControl interface, giving more control over machining behavior.
Benefits: By manually setting the machine and process limits, users can reduce physical forces in situations such as weak clamping, ensuring machining safety and optimizing the overall process.
3-Axis Finishing | Mesh Finishing
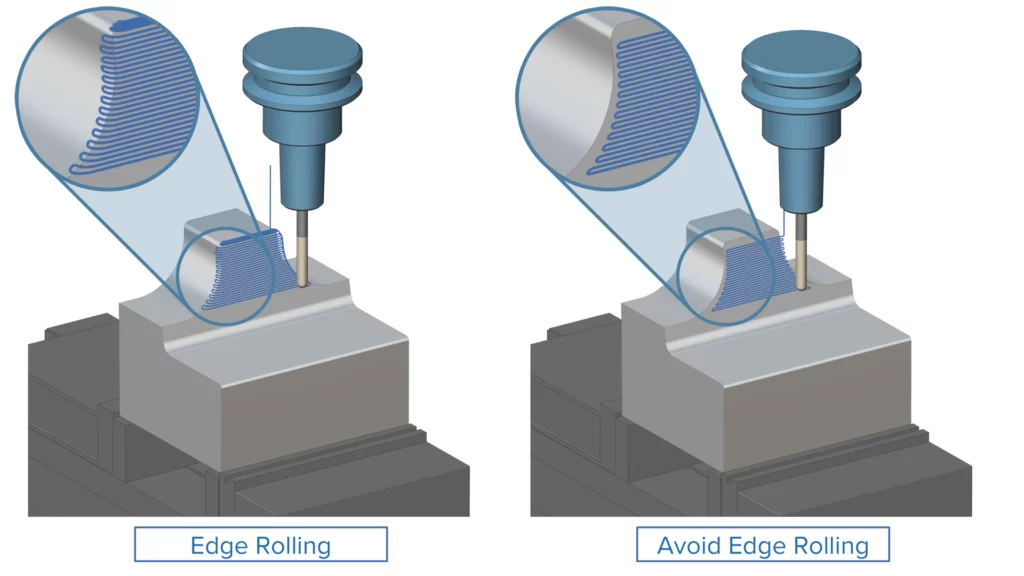
Avoid Edge Rolling
Challenge: In Mold and Die manufacturing, sharp edges are critical design features that must remain untouched during machining. Traditional toolpaths may unintentionally smooth or round these edges, affecting part functionality.
Solution: The refined Avoid Edge Rolling feature ensures that adjacent surfaces are machined accurately while the sharp edge itself is preserved. The toolpath avoids crossing over the edge, maintaining its original geometry.
Benefits: This improvement helps maintain the integrity of sharp edges where they are functionally required, resulting in better part quality and precision. It reduces the risk of unwanted edge rounding and supports consistent, high-quality Mold and Die production.
3-Axis Finishing | Mesh Finishing
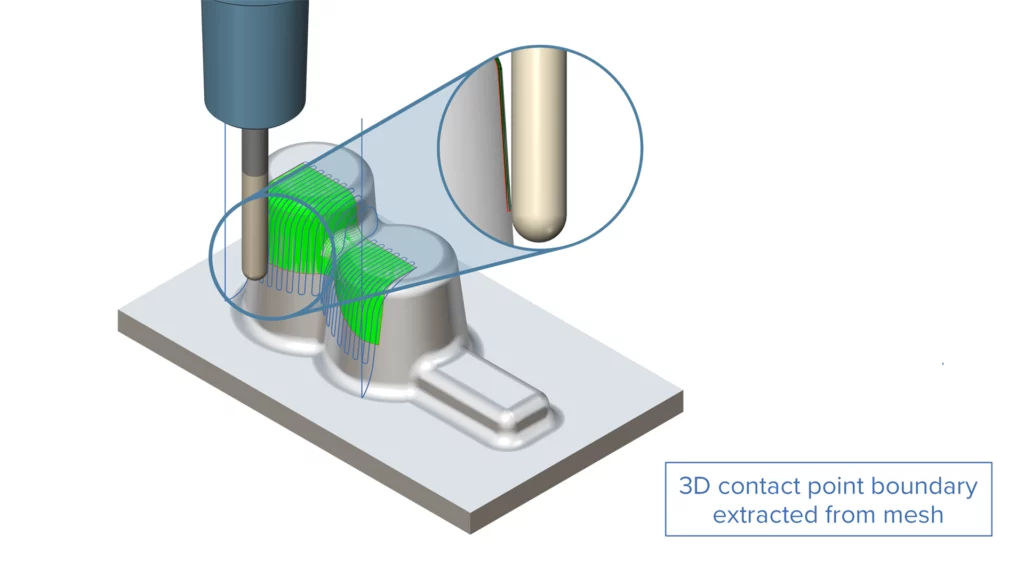
3D Contact Point Boundary from Mesh
Challenge: Generating the correct 2D containment while following all rules for 3D Contact Point Boundary recognition was a time-consuming manual process, especially when the chaining direction did not align with the desired machining area.
Solution: This release introduces an option to directly extract the 3D Contact Point Boundary from a mesh.
Benefits: This new feature makes programming more convenient and consistent.
3-Axis Finishing | Corner Finishing
New Corner Finishing
Challenge: Machining internal corners in Molds and Dies often requires smaller, longer cutting tools with reduced rigidity and greater risk of breakage. To overcome this, the toolpath would need to find and remove all of the unmachined stock safely, while also removing the need for subsequent processing or hand polishing.
Solution: The new Corner Finishing toolpath accurately identifies areas that contain remaining material. It avoids unnecessary repositioning and machines steep and shallow areas with separate, dedicated cut patterns.
Benefits: This dedicated corner finishing strategy safely and effectively removes all material, delivering enhanced surface quality and reducing the need for subsequent hand processing.
3-Axis Roughing | Adaptive Roughing
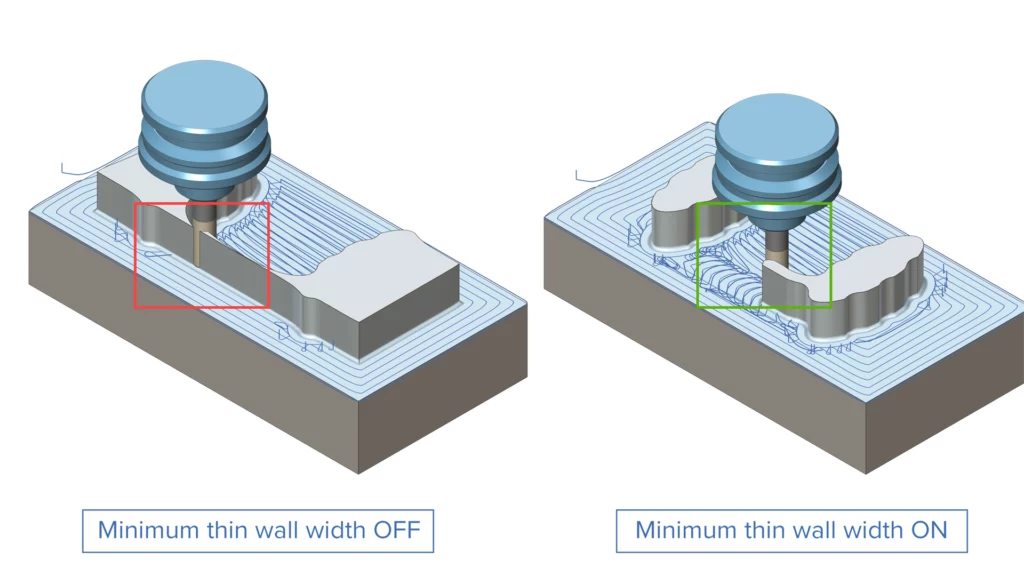
Thin Wall Avoidance for Adaptive Roughing
Challenge: In Adaptive Roughing, a key challenge is the unintentional creation of thin, unsupported walls. These weaken under cutting forces, causing vibration, unpredictable tool loading, faster wear and a higher risk of tool failure.
Solution: Now, the minimum stock wall thickness can be controlled during processing. Once the tool breaks through the remaining stock wall, all subsequent machining is performed with optimal tool engagement.
Benefits: The introduction of this feature eliminates the formation of thin walls, maintaining stable tool loading during machining and significantly extending tool life.
Discover the many other new enhancements in this release.