Software Release 2025.12
Other Enhancements
This release also introduces a host of enhancements across the entire ModuleWorks portfolio, driving further advancements in toolpath, simulation and automation technologies. These improvements deliver higher performance, enhanced flexibility and more efficient workflows, enabling users to maximize productivity and efficiency.
Toolpath
Multi-Axis Roughing | Area Roughing
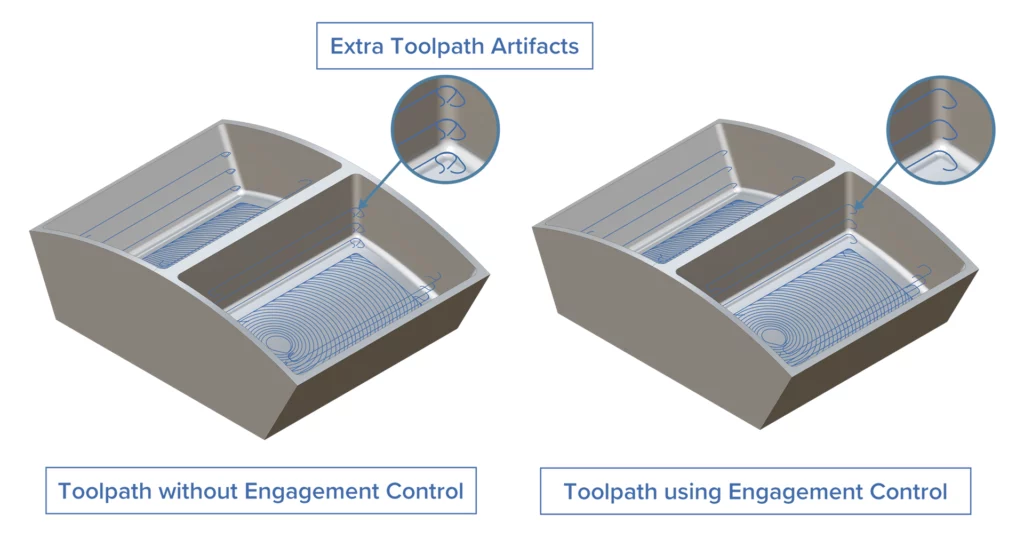
Engagement Control for Intermediate Slices
Challenge: Without engagement control, intermediate slices are generated with only a minimum amount of material to remove, especially in the inner corners. This leads to inefficient tool motion and increased non-cutting time.
Solution: A new user-defined parameter limits or adjusts the tool engagement threshold for intermediate slices. When the tool engagement falls below the defined threshold, the system defers material removal to a final boundary pass.
Benefits: This helps to eliminate unnecessary toolpath artifacts for more efficient stock removal and faster machining. It also extends tool life due to optimal engagement and enhances toolpath quality in tight geometries.
Multi-Axis Roughing | Area Roughing
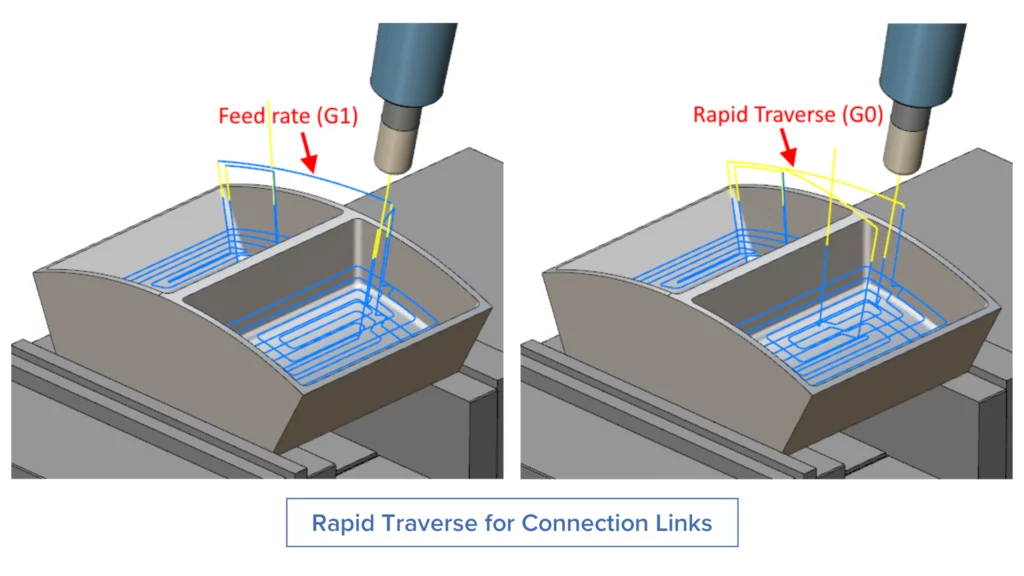
Rapid Traverse for Connection Links
Challenge: Due to the fallback sequence mechanism, all “Feed distance” connection moves retracted up to the “Rapid distance” height. In these situations, the connection moves were executed at feed rate (G1) instead of rapid rate (G0).
Solution: With this new feature, all the connection moves are now performed at the rapid rate (G0).
Benefits: This new feature gives users enhanced control over the feed rates on connection moves, enabling faster machining.
3-Axis Finishing | Mesh Finishing
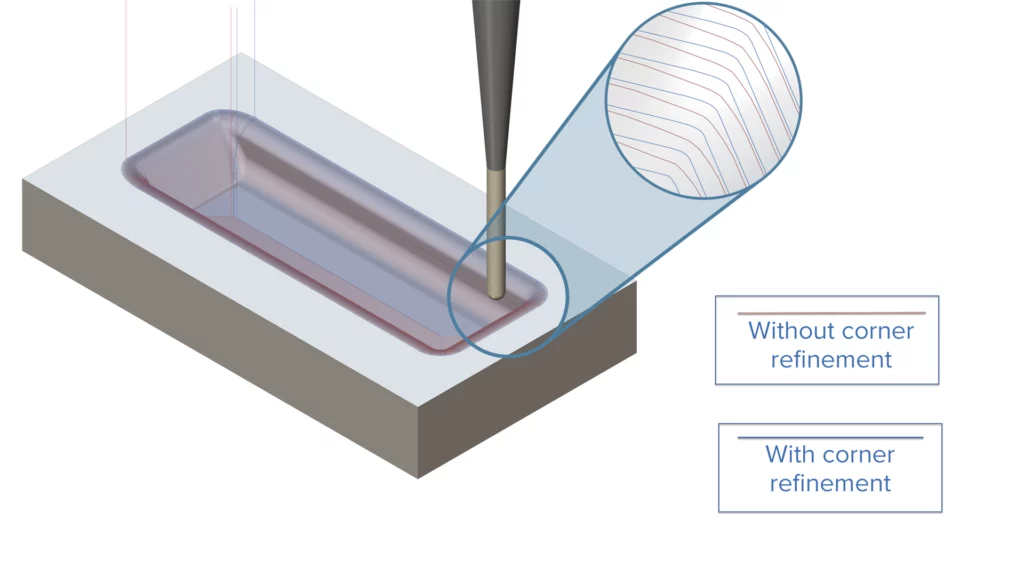
Corner Refinement for Constant Cusp Pattern
Challenge: Inconsistencies in creating the cut pattern can lead to missed areas on the part and poor surface quality.
Solution: By employing enhanced propagation algorithms with targeted refinement in corner generation, the process yields superior geometric accuracy and results in a cleaner, more consistent surface finish.
Benefits: This new feature achieves a superior surface quality without compromising the stepover or cut tolerance, thereby eliminating the need to compensate for inaccuracies in the toolpath pattern.
3-Axis Finishing | Mesh Finishing
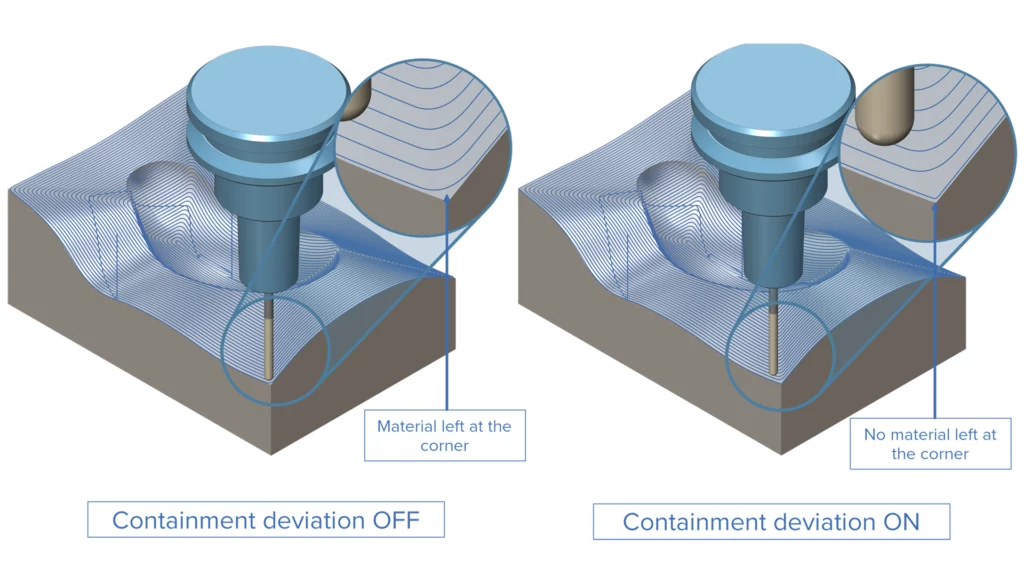
Deviation for Containment Cuts
Challenge: When the smooth corner option is applied to offset toolpaths, it also influences the first and last cuts on the containment, which can result in leftover material.
Solution: A separate deviation setting for containment cuts has been introduced to effectively remove leftover material.
Benefits: This enhancement improves surface quality and gives users the flexibility to remove excess material within the same operation.
3-Axis Finishing | Mesh Finishing
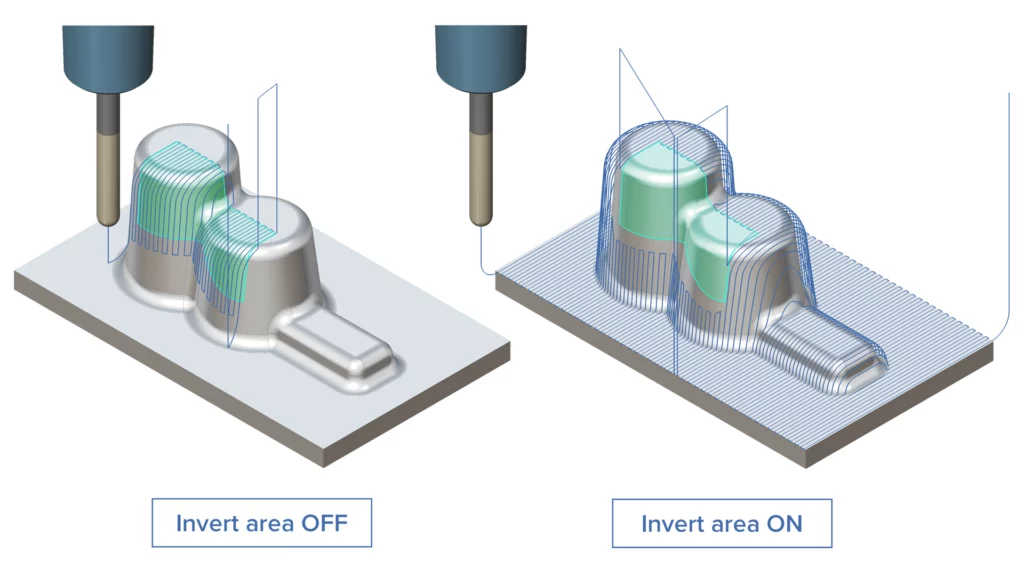
Invert Machining Area for 3-Axis Finishing
Challenge: Previously, the 3D Contact Point Boundary machining area was determined by the chaining direction of the geometry input. If the chosen direction did not produce the desired machining area, it had to be inverted manually.
Solution: Now, there is an option to invert the machining area.
Benefits: This new option makes the programming process more convenient and efficient.
3-Axis Finishing | Mesh Finishing
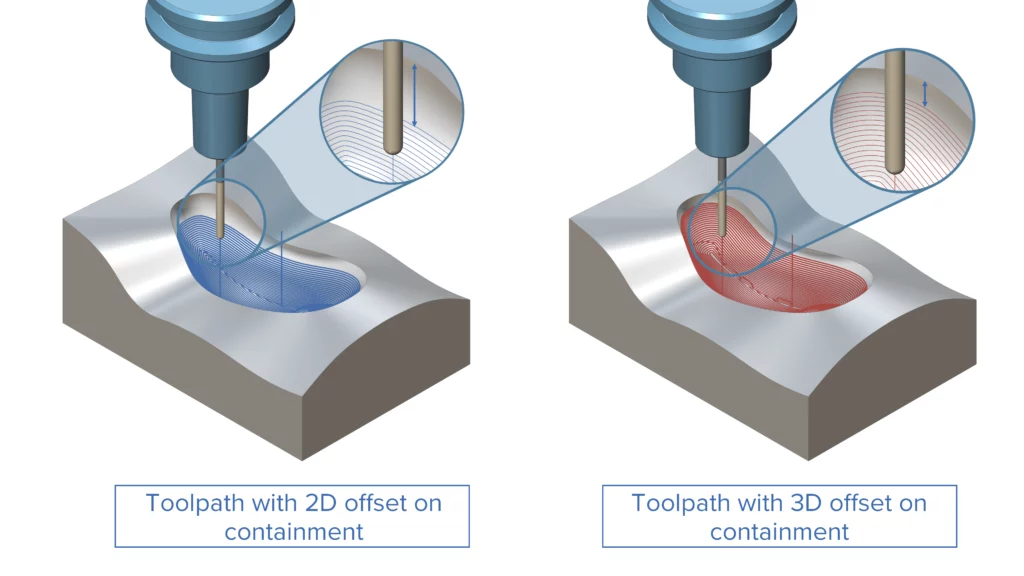
3D Offset for Containment
Challenge: The common offset from the containment, which is first shifted in 2D space and then projected onto the surfaces, can lead to an inconsistent toolpath offset on the part, depending on the inclination of the surfaces involved.
Solution: ModuleWorks 2025.12 solves this with the new 3D Offset for Containment option.
Benefits: 3D Offset for Containment generates an offset along the part, providing greater control over the offset results.
3-Axis Finishing | Mesh Finishing
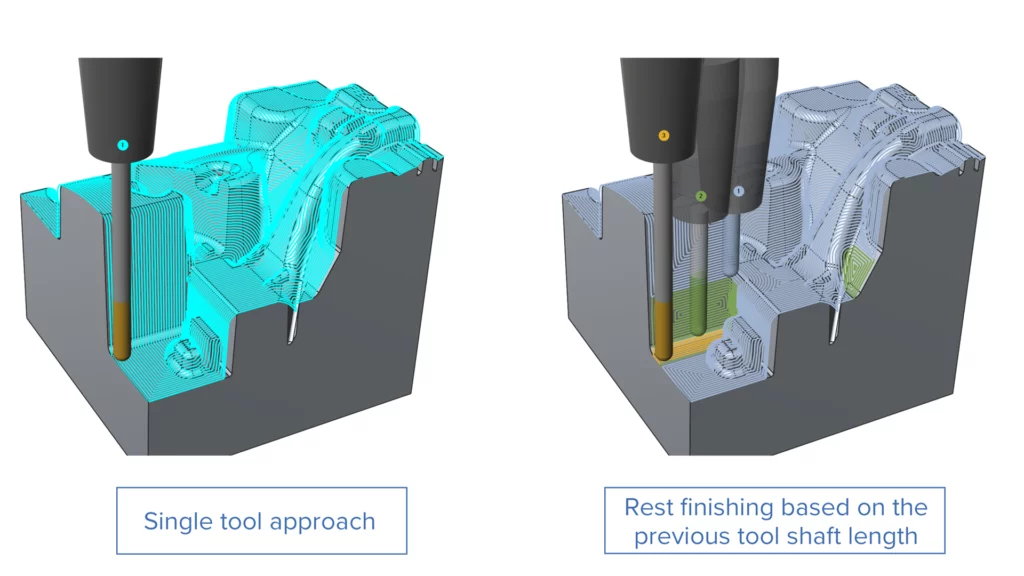
Rest Finishing Based on Shaft Length for Constant Cusp
Challenge: For deep core and cavity parts, it is common to split the operation into multiple steps based on the tool’s stick-out length. However, creating a rest finish operation with a long tool is difficult when the part has already been partially machined using a shorter stick-out length.
Solution: A new option automatically detects areas left unmachined by a shorter tool and machines them using a longer stick-out. This was already possible for other strategies and is now also available for the Constant Cusp pattern.
Benefits: This feature enhances the quality of the machined part while significantly reducing programming time.
3-Axis Roughing | Adaptive Roughing
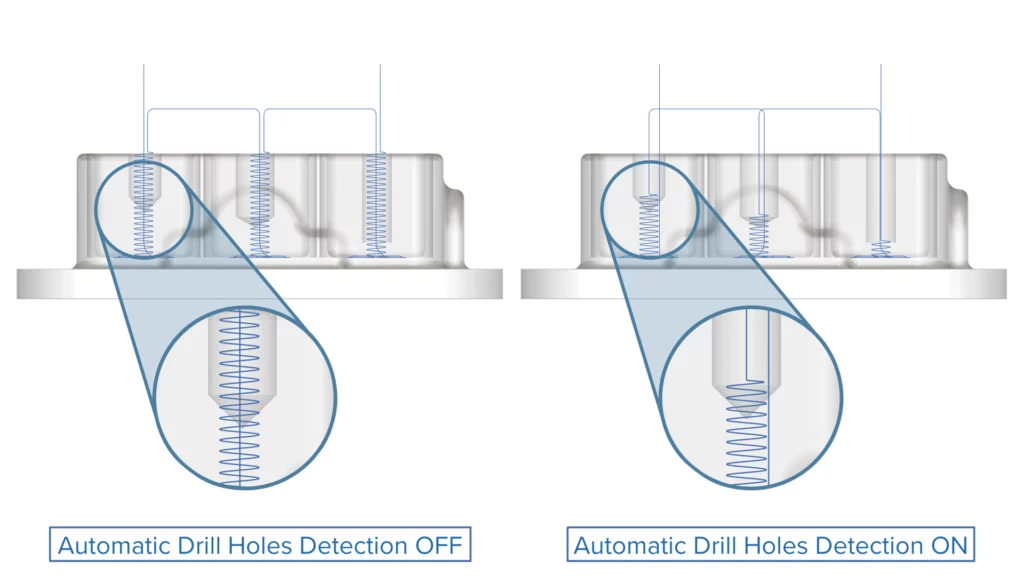
Automatic Drill Holes Detection
Challenge: Previously, users had to manually define each pre-drill hole, even when the stock already contained them. This made the “Pre-drill” option time-consuming and difficult to use.
Solution: Automated detection of existing drill holes is now supported, along with geometry-aware toolpath generation that intelligently adapts ramp heights and approach paths.
Benefits: This enhancement significantly reduces programming effort, improves toolpath safety and minimizes air cuts, resulting in faster setup and better machining performance.
3-Axis Roughing | Offset/Parallel Roughing
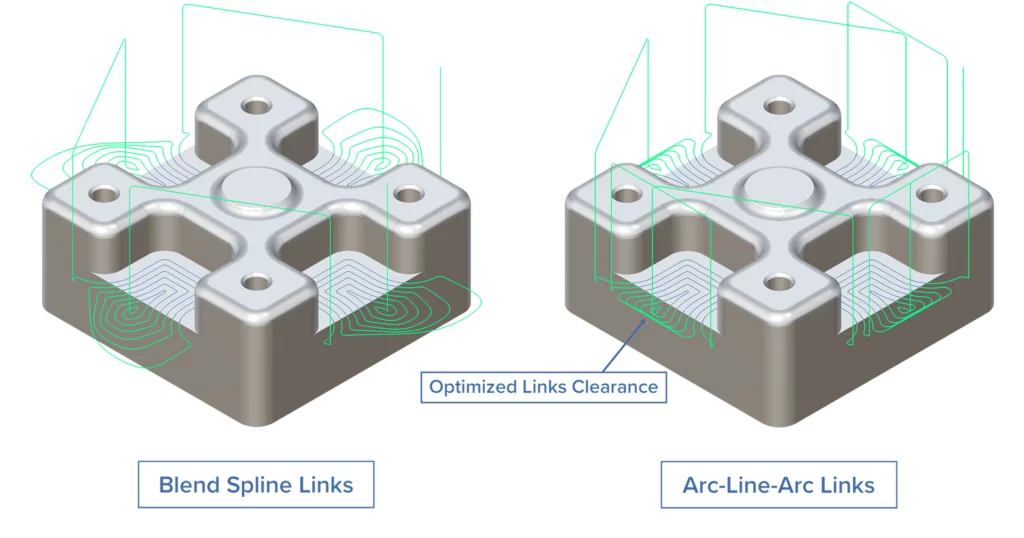
Arc-Line-Arc Links for Offset Roughing
Challenge: Until now, using blend spline links was the only way to create smooth toolpath links at the current slice level. However, the farther apart the start and end points of adjacent roughing passes were, the further away from the part these blend spline links were generated.
Solution: This new “Arc-Line-Arc” option for area links provides smooth toolpath linking at the current slice level.
Benefits: This new feature ensures smooth toolpath linking at the current slice level, optimizing the distance to the outer boundary of the part. This reduces both air cuts length and processing time.
3-Axis Roughing | Offset/Parallel Roughing
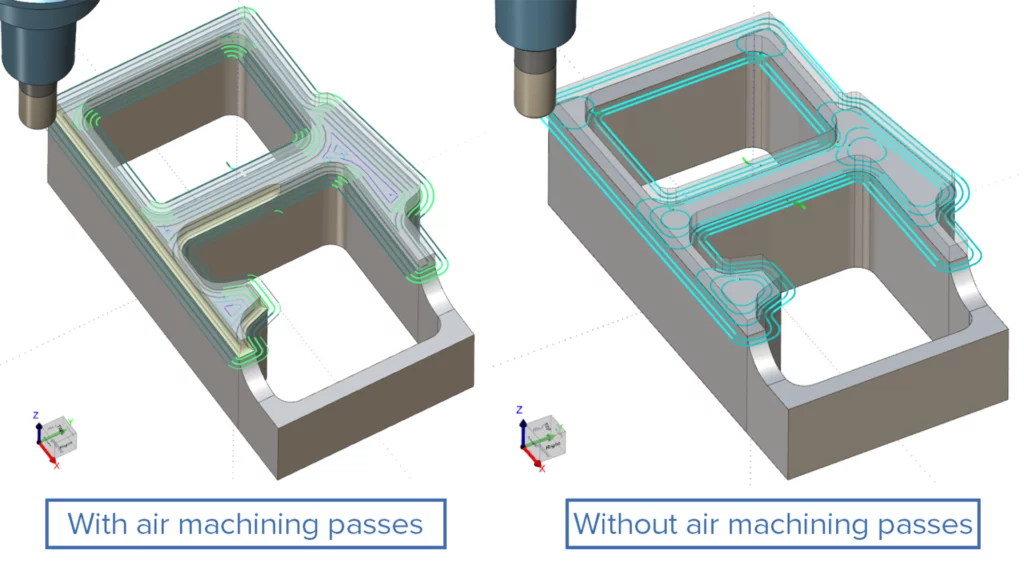
Improved "Avoid Air Machining" Algorithm
Challenge: The previous “Avoid Air Machining” approach relied on filtering toolpath contours using inscribed circle criteria. This method often missed certain tool coverage areas, leading to undetected regions, inefficient air cuts and unnecessary machining time.
Solution: The enhanced “Avoid Air Machining” logic uses advanced detection of overlapping tool coverage areas, dramatically cutting down on unnecessary tool movements in empty regions and greatly boosting machining efficiency.
Benefits: The new “Avoid Air Machining” algorithm provides:
– Smart detection of overlapped regions
– Optimized toolpath generation
– Reduced machining time with equivalent results
2-Axis Machining
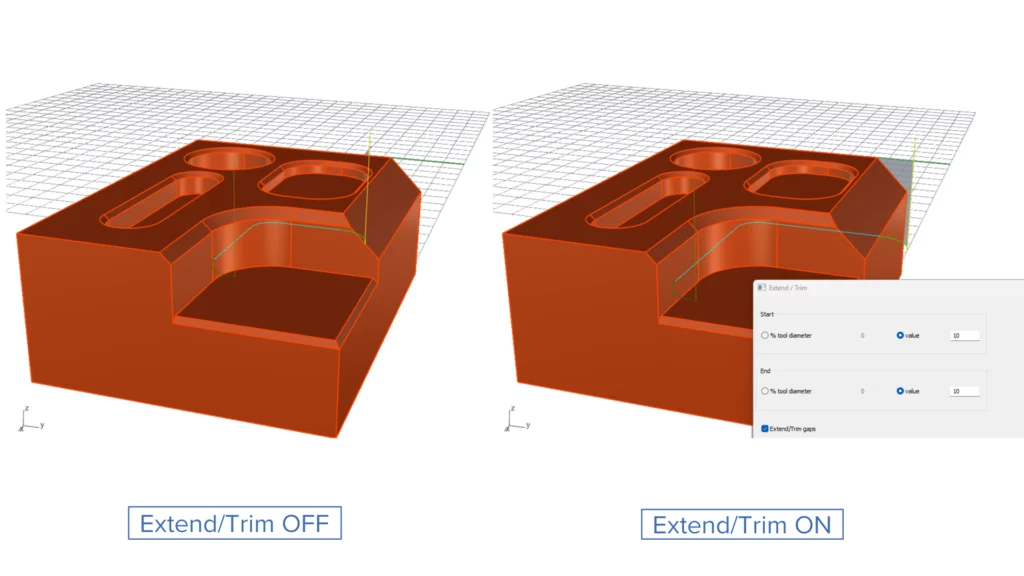
Extend/Trim for 2-Axis Wireframe Chamfer
Challenge: Since the stock and offset vary from one operation to another, the tool needs extra safety when engaging the material.
Solution: This new feature makes the toolpath extension and toolpath trimming options available for 2-axis wireframe chamfer operations.
Benefits: Users are now able to ensure additional safety during tool engagement as well as consistent leads. It also makes the 2-axis wireframe chamfer options consistent with the other wireframe options.
2-Axis Machining
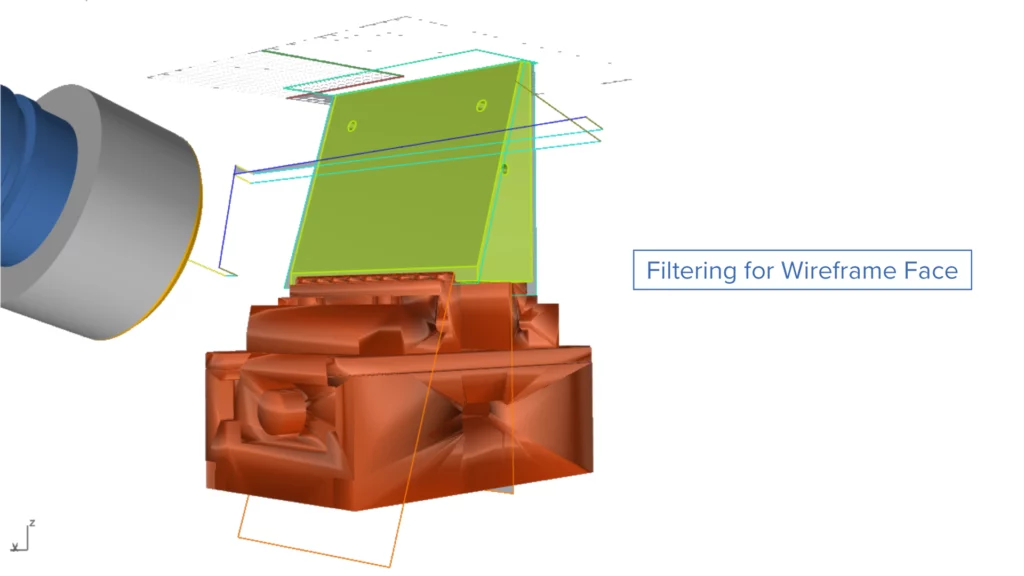
Filtering for Wireframe Face
Challenge: When using fixtures, certain areas might require a very small cut move. However, it is sometimes preferable to ignore this small cut and use a different process later.
Solution: With this new feature, users can easily remove small toolpath cuts that would otherwise require the creation of additional geometries.
Benefits: Eliminating the need for extra geometries reduces the number of air moves and speeds up the machining process.
Turning | High Dynamic Turning
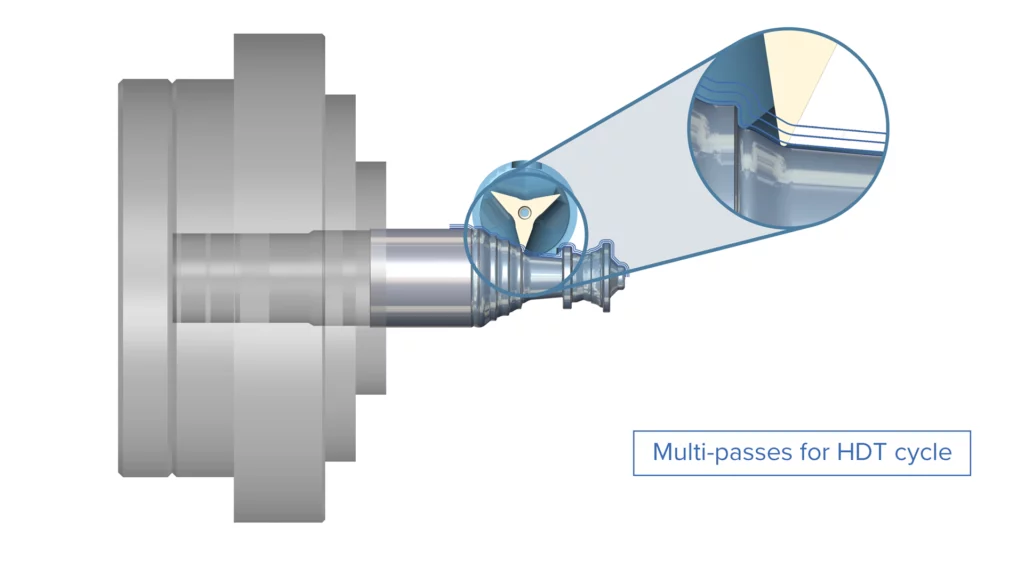
Multi-Passes for High Dynamic Profile Cycle
Challenge: When the remaining stock for finishing is uneven or excessive, users previously had no option for multiple finishing passes, forcing them to resort to cumbersome methods and manual effort.
Solution: This new option enables users to apply multiple finishing passes.
Benefits: Applying multiple finishing passes delivers superior surface quality by gradually removing remaining material. It also prevents the tool from overloading during the finishing operation, as the workload is distributed across several lighter passes. This improves tool life and ensures consistent results.
Turning | Turning Basic
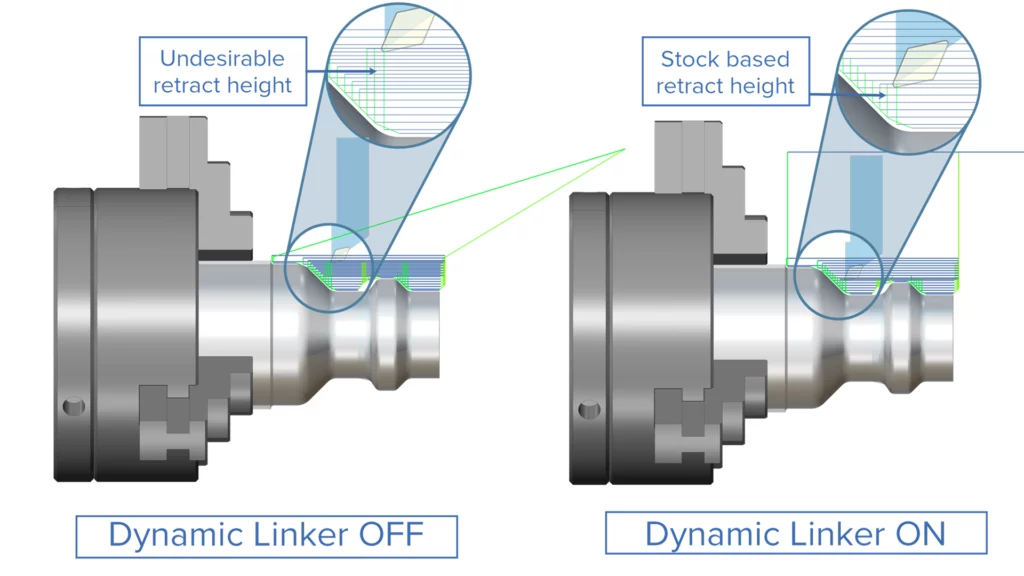
Dynamic Linker for Rough Turning Strategies
Challenge: A frequent challenge with standard linking is repositioning from one cut region to another. This is because links are generated at a safe distance rather than optimized for the current in-process stock, resulting in unnecessary and inefficient machine motions.
Solution: The new “Optimized Lead and Link distances” option dynamically evaluates the current in-process material and generates safe and efficient repositioning movements between regions, helping to avoid collisions and minimizing total machining cycle time.
Benefits: The use of optimized, dynamic links reduces cycle times, cuts down on unnecessary air moves, ensures connecting links are efficient, and creates collision-free toolpaths by taking the in-process stock into consideration.
Turning | Turning Basic
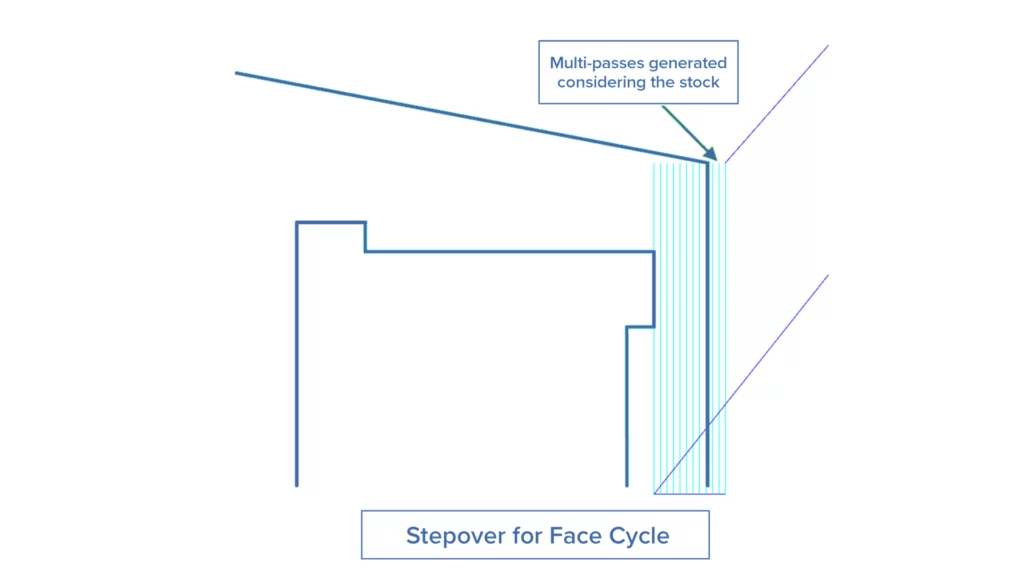
Stepover for Face Cycle
Challenge: Users were able to apply multi-passes to the face cycle, but these passes did not consider the input stock.
Solution: With this new feature, users can now include the input stock when generating multi-passes for the face cycle ensuring the in-process material is considered regardless of its complex geometry.
Benefits: This feature eliminates the need for manual calculations by incorporating the input stock into multi-pass facing operations. It also supports complex applications that require specialized support of the in-process workpiece.
Simulation
Simulation Systems | NC Editor
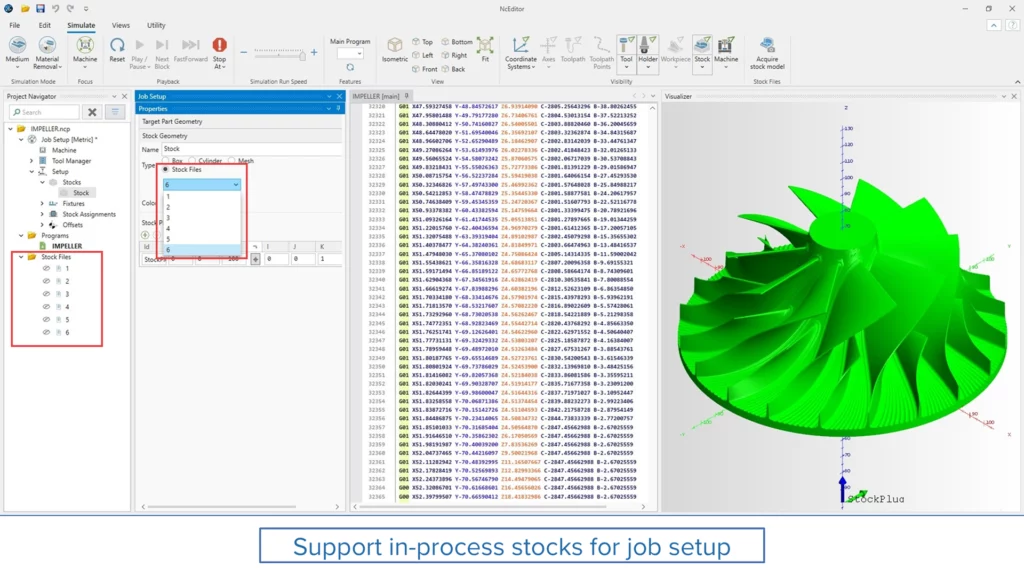
Support for In-Process Stocks in Job Setup
Challenge: Previously, users had to manually export and re-import stock files to use them in subsequent setups. This was time-consuming, prone to errors and led to increased setup time.
Solution: A new interface in job setup enables direct selection of in-process stock files, eliminating the need for manual file handling and improving workflow continuity.
Benefits: This enhancement simplifies multi-setup programming, reduces setup time, and improves overall efficiency by allowing seamless reuse of pre-machined stock data.
Additive
Additive | Fused Deposition Modeling
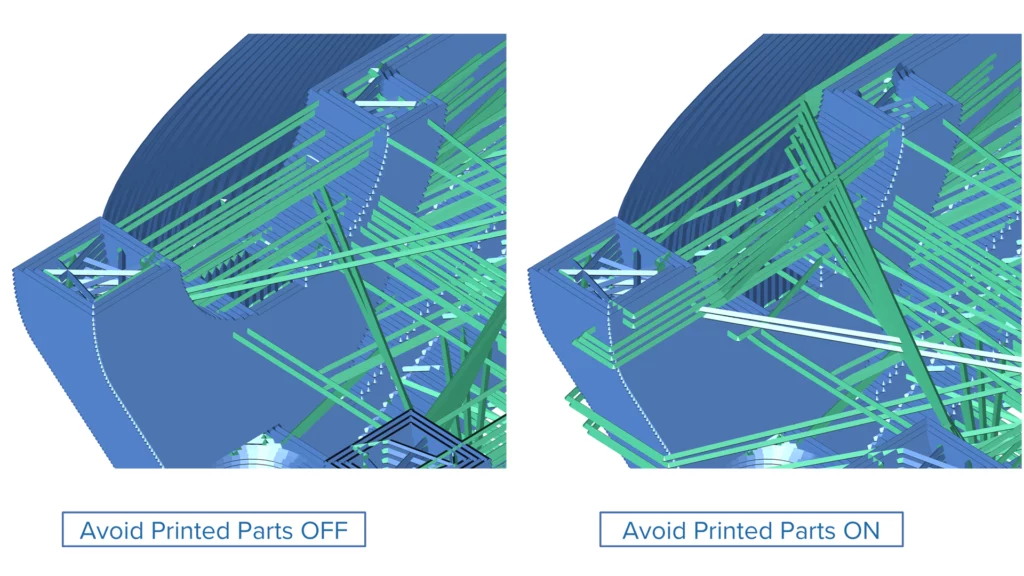
Avoid Printed Parts
Challenge: Standard toolpath strategies prioritize collision-free and time-efficient movements. However, in extrusion processes, especially with viscous materials, these paths can lead to excess material being deposited on finished areas, affecting the surface quality.
Solution: The system now tracks printed regions and intelligently avoids them during link movements. Although this can result in slightly longer paths, it ensures cleaner prints and a better surface finish.
Benefits: This enhancement improves the quality and surface finish of parts by avoiding unintended material accumulation on printed areas.
Additive | Fused Deposition Modeling
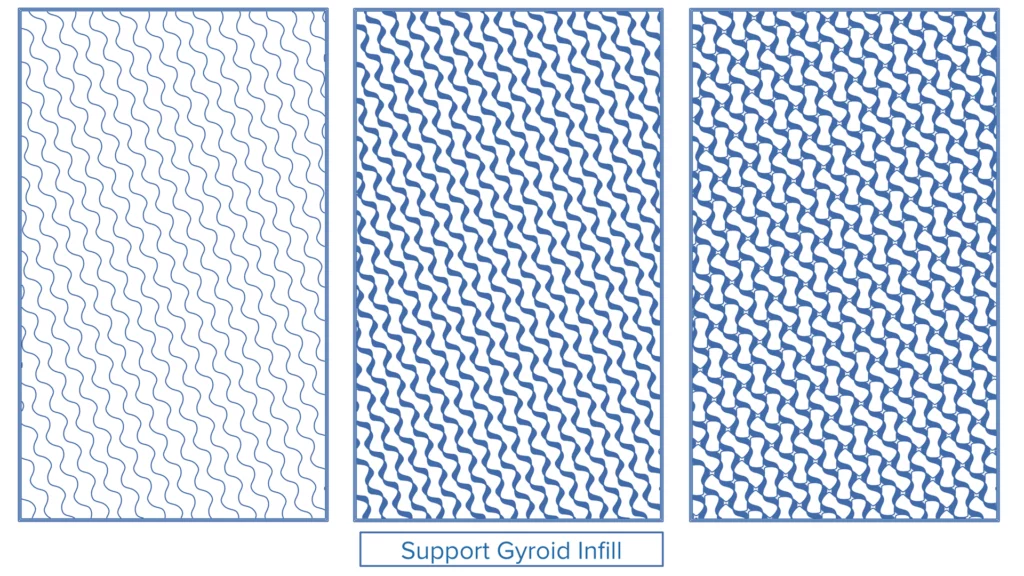
Gyroid Infill
Challenge: The gyroid pattern is mathematically complex, composed of wavy lines that rotate across slices. Calculating density and generating paths based on standard parameters posed a challenge for accurate and efficient implementation.
Solution: The gyroid structure is now generated using a mathematical formula that adapts to user-defined infill density and path widths. This enables precise control over the pattern while maintaining its mechanical benefits.
Benefits: This enhancement delivers greater rigidity, improved dimensional accuracy and better mechanical performance.