Successful remanufacturing through data-based decision-making and intelligent process planning
Funding agency: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)/ Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Production and Manufacturing Technologies Division (PTKA-PFT)

Project Number: 02J21E110
The project “EREP” is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BWBF) and the Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Production and Manufacturing Technologies Division (PTKA-PFT) under the project no.: 02J21E110.
Details
Recent environmental and political crises require drastic energy savings and the wide implementation of the circular economy. Remanufacturing, meaning the refurbishment of old or worn parts, is one of the key components of the circular economy. Within this context, the project EREP aims to increase the resilience of production by expanding the application of remanufacturing through a hybrid process chain. With the further application of data-based methods process planning will become more efficient. The result is an extensive process chain for remanufacturing that has been extended by additive processes.
Supply chains have been severely disrupted in recent years due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russian war against Ukraine. A production efficient in resources and energy is thus no longer just a question of environmental considerations, but also of the prosperity and independency of Europe in general and Germany in particular. An important step in this direction is implementation of the circular economy which uses principles such as the re-use and recycling of goods. Apart from re-using and recycling, remanufacturing is one of the key aspects of the circular economy. It describes the refurbishment process of old or worn parts. By now, remanufacturing can be supported with the help of industry 4.0 technologies and realized with minimal energy requirements.
Following from this, the project EREP aims the increase the resilience of production, particularly with elements of hybrid production chains. Within the project, these serve as the expansion of remanufacturing, helping to establish the circular economy. With the application of data-based methods for decision-making and process planning, the implementation should become more efficient.
Hybrid process chains combine additive and subtractive processes. Additive processes serve the application of material, for example to enrich worn areas or holes with additional material. Subtractive processes involve the removal of material and complement additive processes to restore the properties of functional surfaces in a precise way.
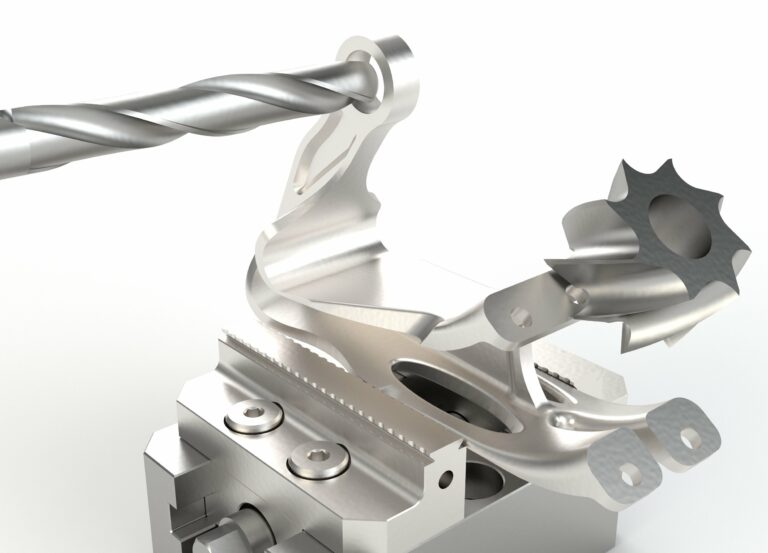
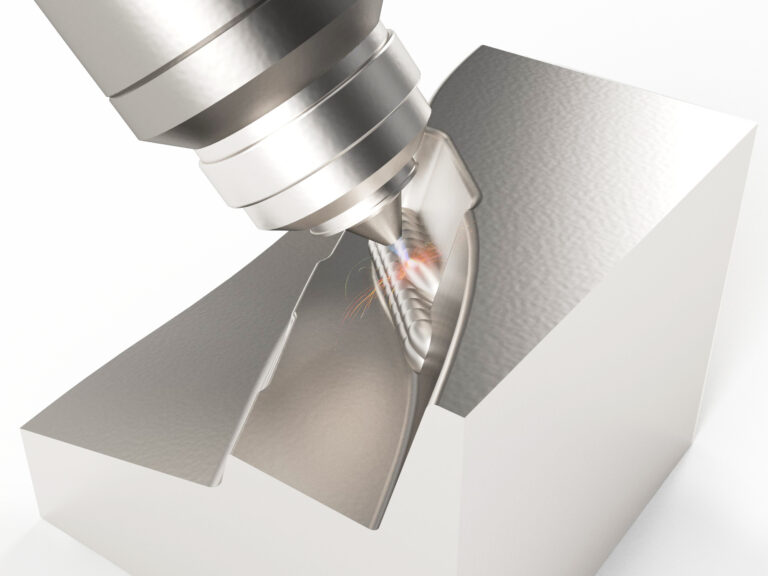

The result is an extensive process chain for remanufacturing that has been extended through additive processes. This chain is accompanied by intelligent software tools that support the process from the initial decision-making process to the completely refurbished part. ModuleWorks is working towards a software solution that calculates the difference between old and new components as well as developing a CAM environment to generate programs for the parts.
Partners
Start: October 2022
End: September 2025